ESP32 rmt_tx simple pulse example (ESP-IDF)
In contrast to our previous example from ESP32 RMT pulse generation minimal example using Arduino & PlatformIO this example uses the new rmt_tx API.
rmt_tx.cpp
#include <driver/rmt_tx.h>example.cpp
rmt_channel_handle_t channel;
rmt_tx_channel_config_t tx_chan_config = {
.gpio_num = GPIO_NUM_19, // GPIO number
.clk_src = RMT_CLK_SRC_DEFAULT, // select source clock
.resolution_hz = 1 * 1000 * 1000, // 1 MHz resolution
.mem_block_symbols = 64, // memory block size, 64 * 4 = 256 Bytes
.trans_queue_depth = 1, // set the number of transactions that can pend in the background
};
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(rmt_new_tx_channel(&tx_chan_config, &channel));
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(rmt_enable(channel));
rmt_symbol_word_t txdata[64];
txdata[0] = {
.duration0 = 100,
.level0 = 1,
.duration1 = 0,
.level1 = 0,
};
// Create simple encoder
rmt_copy_encoder_config_t encoder_config;
rmt_encoder_handle_t encoder;
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(rmt_new_copy_encoder(&encoder_config, &encoder));
rmt_transmit_config_t tx_config = {
.loop_count = 0, // no transfer loop
};
while(true)
{
ESP_ERROR_CHECK(rmt_transmit(channel, encoder, pulseRMT, 1*sizeof(rmt_symbol_word_t), &tx_config));
// Wait for one second
vTaskDelay(10 / portTICK_PERIOD_MS);
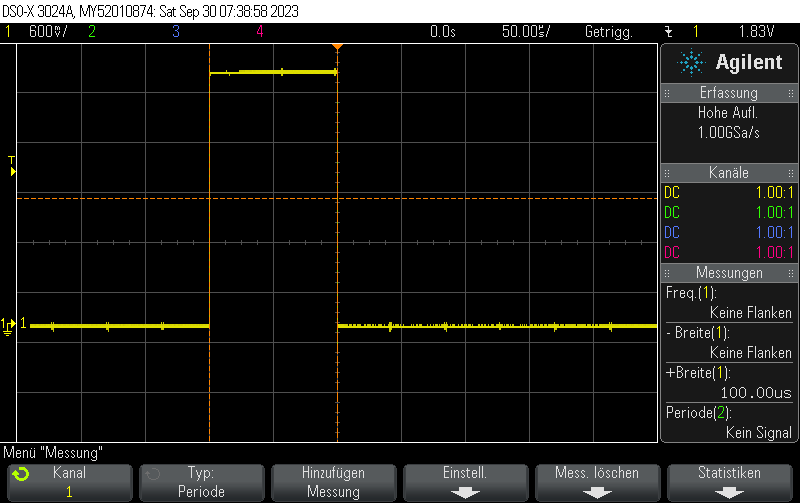
}Result:
Check out similar posts by category:
ESP8266/ESP32
If this post helped you, please consider buying me a coffee or donating via PayPal to support research & publishing of new posts on TechOverflow