Matlab Level 2 S-Function example: Sine wave (continous output)
Just place the following file in your Matlab path (e.g. the directory open in Matlab/Simulink) and run mex sfun_sine_wave.cpp to compile it. It generates a 1 Hz sinewave at 1 kHz sampling rate.
sfun_sine_wave.cpp
#define S_FUNCTION_NAME sine_wave_generator
#define S_FUNCTION_LEVEL 2
#include "simstruc.h"
#include <cmath> // For sine wave generation
// Define constants
#define SAMPLING_RATE 1000 // 1kHz
#define WAVE_FREQUENCY 1 // 1Hz
#define PI 3.14159265358979323846
// Function: mdlInitializeSizes ===============================================
// Abstract:
// Setup sizes of the various vectors.
static void mdlInitializeSizes(SimStruct *S)
{
ssSetNumSFcnParams(S, 0); // No parameters
ssSetNumContStates(S, 0); // No continuous states
ssSetNumDiscStates(S, 0); // No discrete states
// 1 output port with 1 element
if (!ssSetNumOutputPorts(S, 1)) return;
ssSetOutputPortWidth(S, 0, 1); // Output port width = 1 (sine wave value)
ssSetOutputPortDataType(S, 0, SS_DOUBLE);
ssSetOutputPortComplexSignal(S, 0, COMPLEX_NO);
// Sample times
ssSetNumSampleTimes(S, 1); // Single sample time
// No work vectors (if needed, allocate work vectors here)
ssSetNumRWork(S, 0); // Real work vector
ssSetNumIWork(S, 0); // Integer work vector
ssSetNumPWork(S, 0); // Pointer work vector
ssSetNumModes(S, 0); // Mode vector
ssSetNumNonsampledZCs(S, 0); // Zero crossings
// Make the S-function block capable of being used in a Real-Time Workshop-generated model
ssSetOptions(S, 0);
}
// Function: mdlInitializeSampleTimes =========================================
// Abstract:
// Initialize the sample times to be 1ms (1kHz)
static void mdlInitializeSampleTimes(SimStruct *S)
{
ssSetSampleTime(S, 0, 1.0 / SAMPLING_RATE); // 1kHz sampling rate
ssSetOffsetTime(S, 0, 0.0);
}
// Function: mdlOutputs =======================================================
// Abstract:
// Calculate the sine wave output based on the simulation time.
static void mdlOutputs(SimStruct *S, int_T tid)
{
real_T *y = ssGetOutputPortRealSignal(S, 0); // Output pointer
real_T time = ssGetT(S); // Get the current simulation time
// Calculate the sine wave value for 1Hz frequency
y[0] = sin(2 * PI * WAVE_FREQUENCY * time);
}
// Function: mdlTerminate =====================================================
// Abstract:
// This function is called at the end of simulation for cleanup.
static void mdlTerminate(SimStruct *S)
{
// No cleanup required for this example
}
// Required S-function trailer
#ifdef MATLAB_MEX_FILE
#include "simulink.c" // MEX-file interface mechanism
#else
#include "cg_sfun.h" // Code generation interface
#endifIn Simulink, you can add it like this:

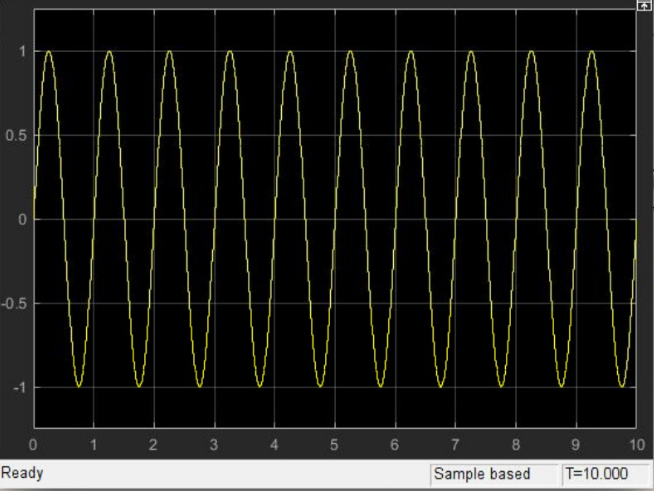
The output, when connected to a Scope, looks like this:
Check out similar posts by category:
Matlab/Simulink
If this post helped you, please consider buying me a coffee or donating via PayPal to support research & publishing of new posts on TechOverflow