import cadquery as cq
obj = cq.Workplane("XY").box(1,1,3)
# Add chamfer to only the top face edges parallel to the X axis
obj = obj.faces("+Z").edges("|X").chamfer(0.2)
obj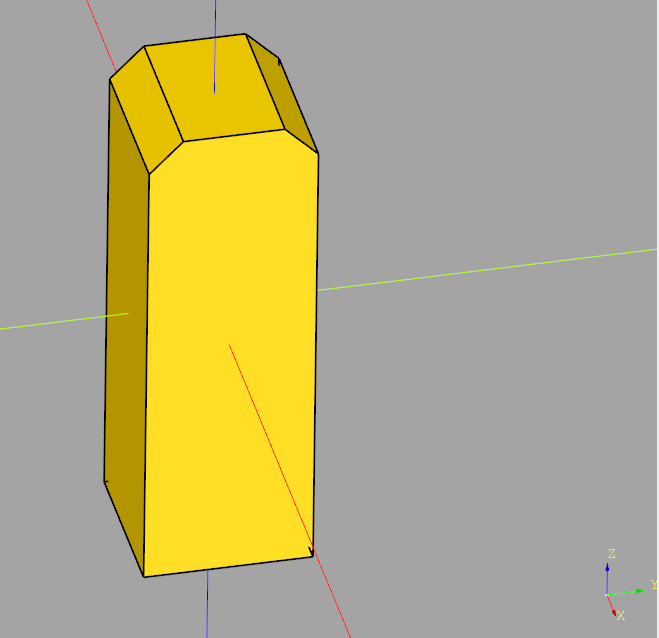
import cadquery as cq
obj = cq.Workplane("XY").box(1,1,3)
# Add chamfer to only the top face edges parallel to the X axis
obj = obj.faces("+Z").edges("|X").chamfer(0.2)
obj
import cadquery as cq
obj = cq.Workplane("XY").box(1,1,3)
# Add chamfer to all top face edges
obj = obj.faces("+Z").chamfer(0.2)
obj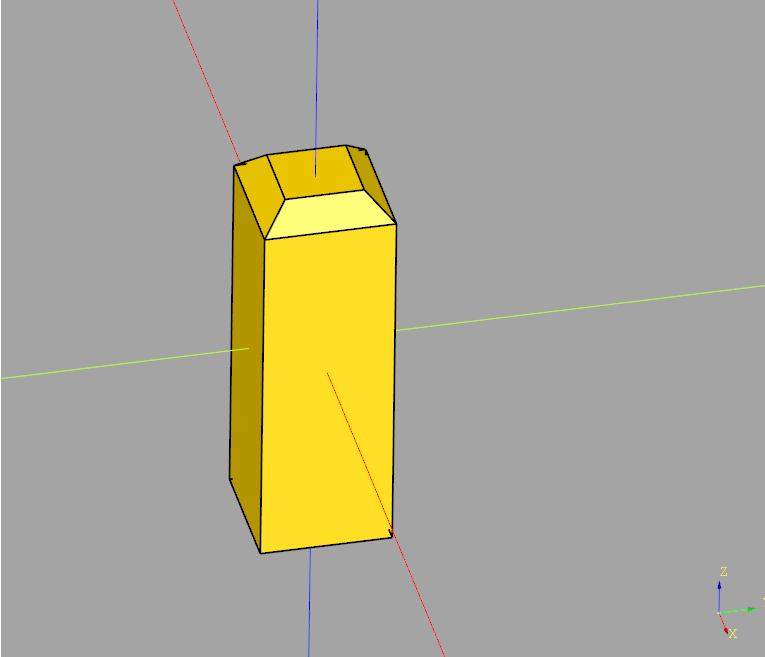
This code chamfers the top side of a sketch rectangle, which is then extruded
import cadquery as cq
obj = (cq.Workplane("YZ")
.sketch()
.rect(1,4)
# Select vertices to chamfer
.vertices(">Y") # Top of local Y coordinate system (which is Z axis)
.chamfer(0.2)
.finalize()
.extrude(0.1)
)
obj
This code creates a sketch from four segment lines forming a rectangle (given the four sets of X/Y coordinates). The segments are then assembled into a face and extruded.
import cadquery as cq
xstart = 1.0
height = 4.0
width = 1.0
obj = (cq.Workplane("YZ")
.sketch()
.segment((xstart, 0), (xstart, height))
.segment((xstart + width, height))
.segment((xstart + width, 0))
.close()
.assemble(tag="face")
.finalize()
.extrude(0.1)
)
obj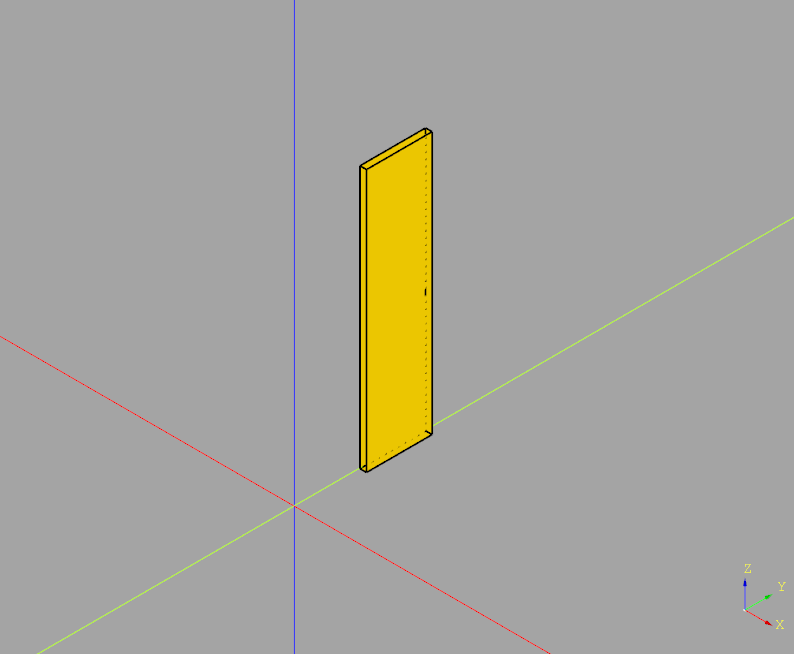
In order to move to a certain position in a CadQuery sketch, use .push(cq.Location(...))
import cadquery as cq
# Create workplane (2d coordinate system for us to create the sketch in)
wp = cq.Workplane("XY")
# Create sketch
result = wp.sketch().push(cq.Location((1,0.5,0))).rect(1,1).finalize().extrude(0.1)
result # This line is just to show the result in cq-editor or jupyter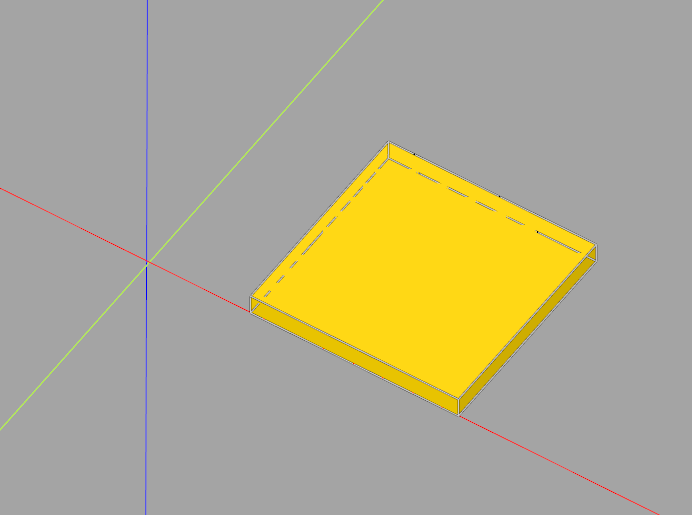
This example generates a 2x2 grid of 1x1mm rectangles in a sketch, then extrudes it
import cadquery as cq
# Create workplane (2d coordinate system for us to create the sketch in)
wp = cq.Workplane("XY")
# Create sketch & extrude
result = wp.sketch().rarray(
1.5, # X distance between center points of rectangles
1.5, # Y distance between center points of rectangles
2, # Number of rectangles in X direction
2 # Number of rectangles in Y direction
).rect(1,1).finalize().extrude(0.1)
result # This line is just to show the result in cq-editor or jupyter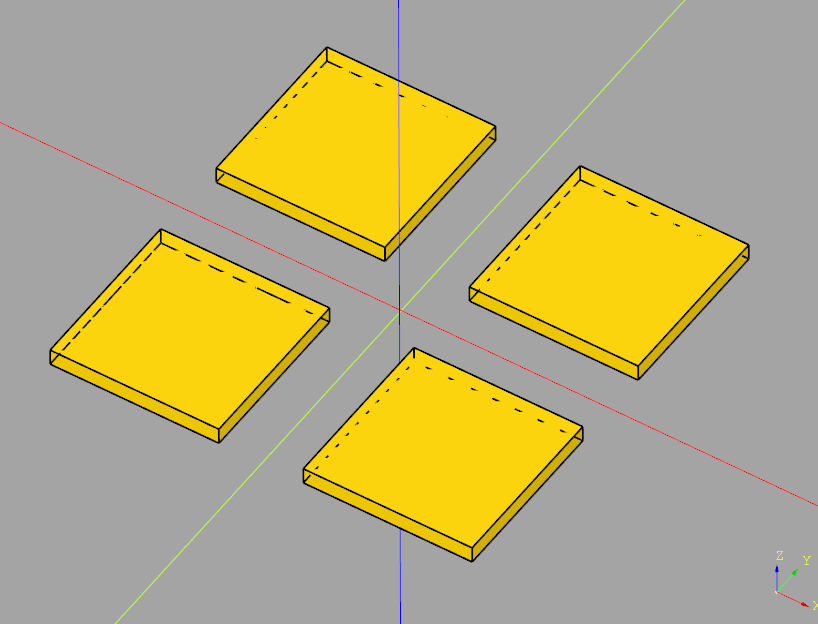
In our previous example CadQuery minimal sketch extrude example we showed how to create and extrude a simple sketch.
You can translate this easily using
result = result.translate(cq.Vector(1,0,0))
import cadquery as cq
# Create workplane (2d coordinate system for us to create the sketch in)
wp = cq.Workplane("XY")
# Create sketch, create rect, close sketch and extrude the resulting face
result = wp.sketch().rect(2, 2).finalize().extrude(0.1)
result = result.translate(cq.Vector(1,0,0))
result # This line is just to show the result in cq-editor or jupyter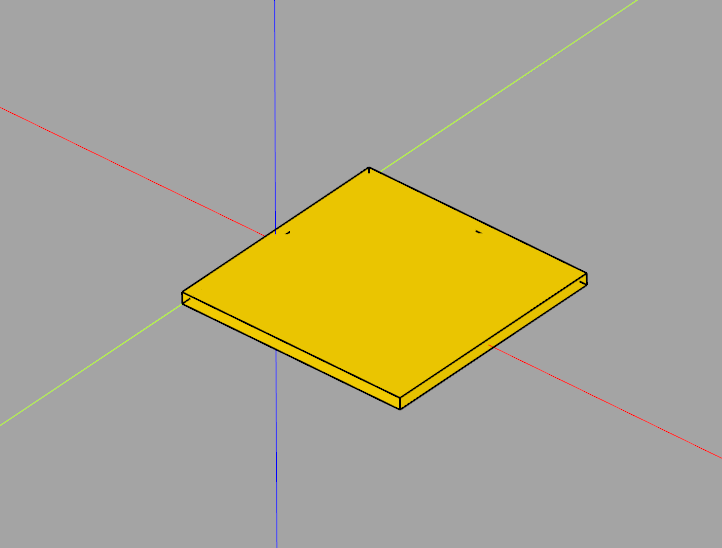
The folllowing example creates a sketch in the XY plane, creates a 2x2mm rectangle in said sketch and extrudes it to a height of 0.1mm.
import cadquery as cq
# Create workplane (2d coordinate system for us to create the sketch in)
wp = cq.Workplane("XY")
# Create sketch, create rect, close sketch and extrude the resulting face
result = wp.sketch().rect(2, 2).finalize().extrude(0.1)
result # This line is just to show the result in cq-editor or jupyter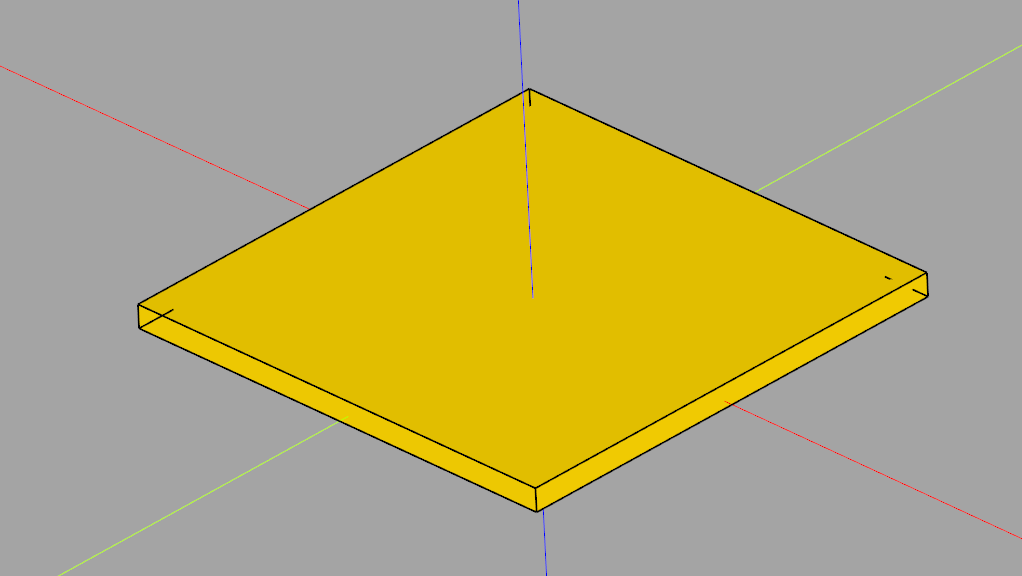
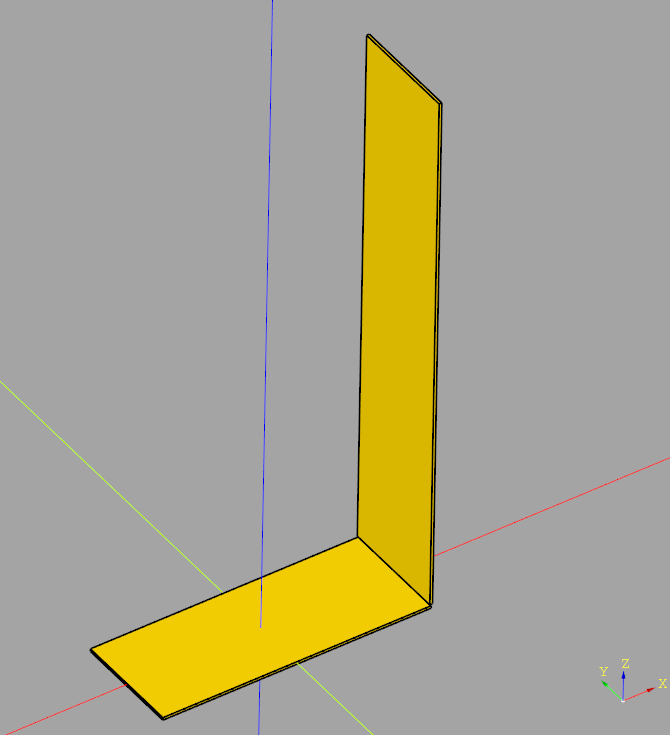
import cadquery as cq
# Define dimensions
base_length = 200 # 20cm
base_width = 80 # 8cm
plate_thickness = 2 # 2mm
upright_height = 400 # 40cm
# Create the base plate
base_plate = cq.Workplane("XY").box(base_length, base_width, plate_thickness)
# Create the upright plate
# Position is set such that it aligns with the end of the base plate and stands upright
upright_plate = cq.Workplane("XY").workplane(offset=plate_thickness).transformed(rotate=(0, 90, 0)).box(upright_height, base_width, plate_thickness).translate((base_length/2, 0, upright_height/2))
# Join the two parts into one
final_part = base_plate.union(upright_plate)
# Export to STEP
final_part.val().exportStep("L-piece.stp")
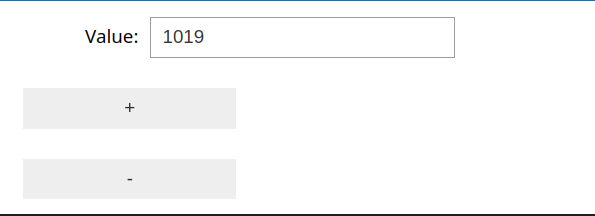
First, define get and set functions:
# Basic examples for get and set value functions
def get_value(): # will only be used to get the initial value
return httpx.get(f"http://{ip}/api/get-value").json()["value"]
def set_value(value):
httpx.get(f"http://{ip}/api/set-value?nedge={value}")
import ipywidgets as widgets
from IPython.display import display
# Step 2: Define the widget components
value_display = widgets.IntText(value=get_value(), description='Value:', disabled=False)
plus_button = widgets.Button(description='+')
minus_button = widgets.Button(description='-')
def on_value_change(change):
set_value(change['new'])
value_display.observe(on_value_change, names='value')
# Step 4: Define the update functions
def on_plus_button_clicked(b):
value_display.value += 1
def on_minus_button_clicked(b):
value_display.value -= 1
# Step 5: Bind the update functions to the buttons
plus_button.on_click(on_plus_button_clicked)
minus_button.on_click(on_minus_button_clicked)
# Step 6: Display the widgets
widgets_layout = widgets
display(value_display, plus_button, minus_button)
This class performs averaging with a fixed time window (variable number of values).
From the platform, it only needs some method to get the current time. This code contains implementations for both ESP-IDF and Arduino
#pragma once
#include <optional>
// Find the correct driver
#ifdef ARDUINO
#include <Arduino.h>
#define TTAA_GETTIME_MILLIS millis()
#elif defined(IDF_VER) && !defined(ARDUINO)
#include <esp_timer.h>
#define TTAA_GETTIME_MILLIS esp_timer_get_time() / 1000
#else
#error "Could not determine how to get the current time (Arduino or ESP-IDF)"
#endif
/**
* @brief This class is designed to accumulate and average values over a specified time threshold.
*
* The class is templated to allow accumulation of different numerical types, defaulting to float. It uses the Arduino `millis()`
* function to track elapsed time, automatically calculating the average of accumulated values once the predefined time threshold is reached.
* The `add()` method adds a new value to the accumulation, returning the average as a `std::optional<T>` when the threshold is reached,
* and `std::nullopt` otherwise. The `lastAverage()` method allows retrieval of the last calculated average at any time.
*/
template<typename T = float>
class TimeThresholdAccumulatingAverager {
public:
/**
* Constructs a new TimeThresholdAccumulatingAverager object.
*
* @param threshold The time threshold in milliseconds over which to accumulate and average values.
*/
TimeThresholdAccumulatingAverager(unsigned long threshold) : _threshold(threshold), _startTime(TTAA_GETTIME_MILLIS), _sum(), _count() {}
/**
* Adds a value to the accumulator. If the time threshold has been reached,
* calculates and returns the average of the accumulated values since the last threshold reset.
* Resets the accumulator for the next period if the threshold is reached.
*
* The given value is not added to the current average if the threshold has been
* exceeded. It is automatically added to the next period's average.
*
* @param value The value to add to the accumulator.
* @return std::optional<T> The average of accumulated values if the threshold is reached, otherwise std::nullopt.
*/
std::optional<T> add(T value) {
unsigned long currentTime = TTAA_GETTIME_MILLIS;
if (currentTime - _startTime >= _threshold) {
// Time threshold exceeded. Calculcate average
T average = _count > 0 ? _sum / static_cast<T>(_count) : 0;
_lastCount = _count;
// Reset sum & count to zero, but add the current value immediatey
_sum = value;
_count = 1;
_startTime = currentTime;
_lastAverage = average;
return average;
} else { // Time threshold not exceeded
_sum += value;
_count++;
return std::nullopt;
}
}
/**
* Returns the average of the last completed accumulation period.
*
* @return T The average value of the last completed period.
*/
inline T lastAverage() const {
return _lastAverage;
}
/**
* Returns the count value of the last completed accumulation period.
*
* @return The last count value.
*/
inline unsigned int lastCount() const {
return _lastCount;
}
private:
unsigned long _threshold;
unsigned long _startTime;
T _sum;
int _count = 0;
T _lastAverage = 0;
unsigned int _lastCount = 0;
};#include <optional>
#include <iostream>
#include "TimeThresholdAccumulatingAverager.hpp"
int main() {
TimeThresholdAccumulatingAverager<float> averager(1000); // 1 second threshold
while (true) {
float newValue = acquireValue(); // Pseudocode for acquiring a new value
auto maybeAverage = averager.add(newValue);
if (maybeAverage.has_value()) {
std::cout << "Average over threshold period: " << average.value() << std::endl;
}
// Add a delay or wait for a real new value in a real application
delay(10);
}
}
The following command recursively removes all .htaccess files from the current directory and all subdirectories:
Please note that the files are deleted directly and not moved to the trash bin, so consider making a backup!
find . -name ".htaccess" -exec rm -v {} \;
((volatile int*)0xFFFFFFFF)[0] = 0;
This will perform an illegal memory access and hence trigger the hard faul. Due to voltatile, it won’t be optimized out by the compiler.
In our previous post STM32H743 DAC rise/fall time experiments we showed that the STM23H743 has relatively long turn-on / turn-off times of approximately 950 nanoseconds, limiting the generation of fast rectangular signals:
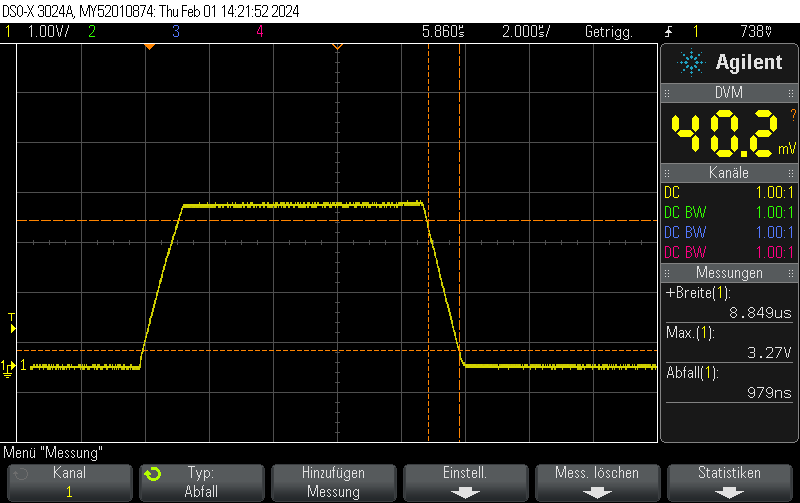
However, there’s a trick how to obtain fall times almost 3 orders of magnitude better for the special case of switching either to full-scale VDD or to GND.
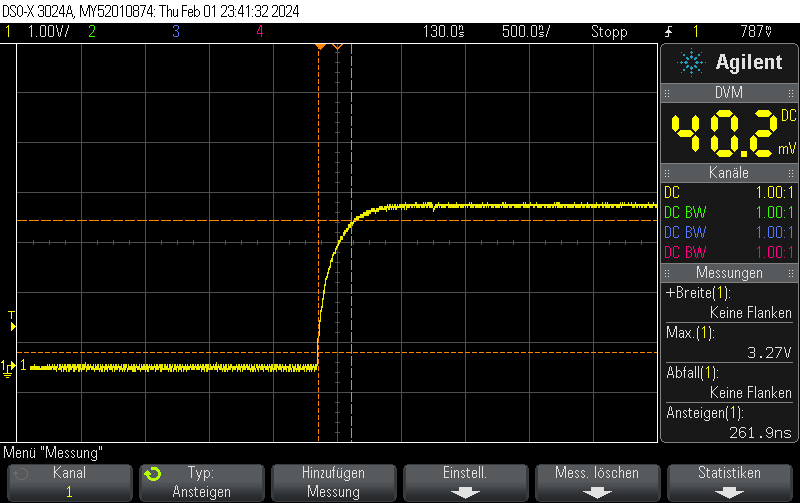
Instead of setting the DAC to the new value, you can just disable the DAC and let the GPIO take care of the rest. This allows for extremely fast fall times of approximately 5ns.
Note that switching the GPIO to digital mode while the DAC is on does not seem to have any effect.
Please note that I didn’t take any care to make the measurement setup immune to the high transients, leading to some oscillation. You should take your own measurements if you have specific requirements.
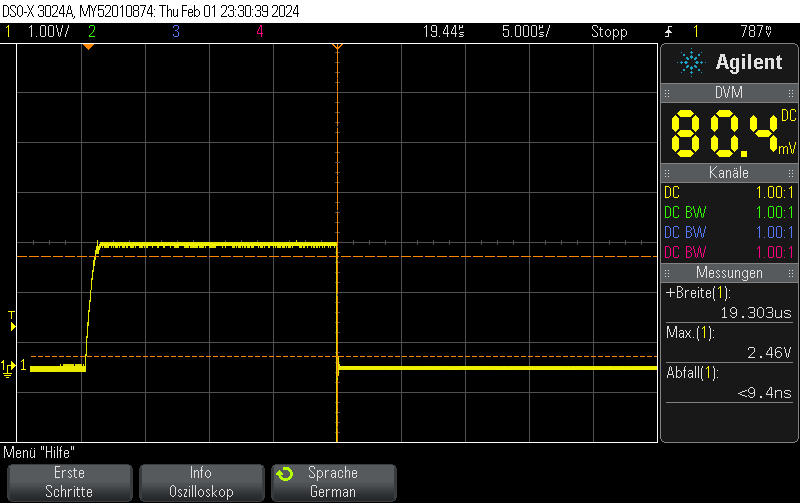
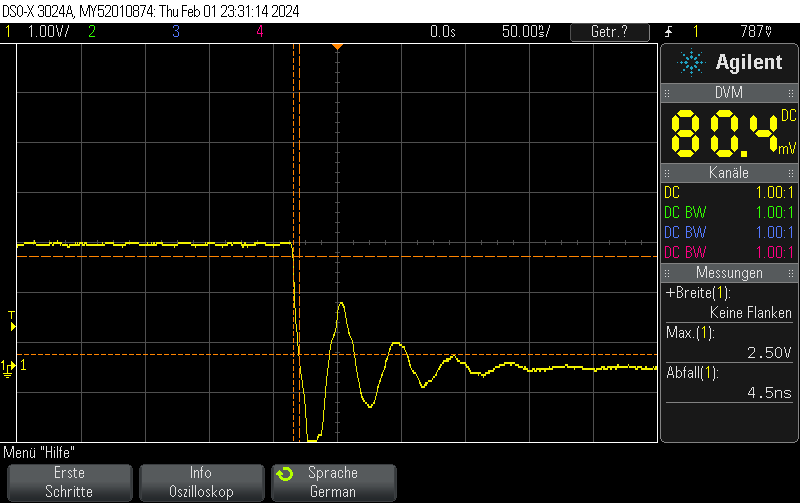
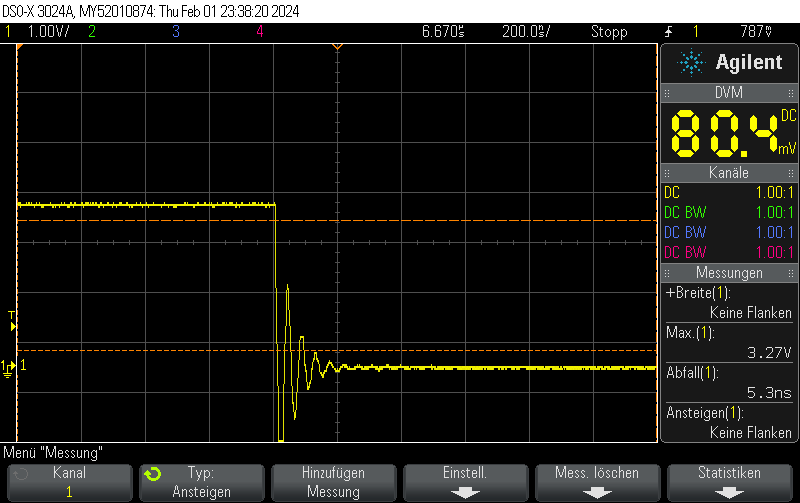
Note that switching on the DAC quickly is outside the scope of this post, but when toggling the DAC enable bit, you can still obtain 250ns rise times pretty easily.
void Init() {
DAC_ChannelConfTypeDef sConfig = {0};
// Initialize DAC
hdac.Instance = DAC1;
if (HAL_DAC_Init(&hdac) != HAL_OK)
{
// Initialization Error
__BKPT();
}
// Configure DAC channel
sConfig.DAC_Trigger = DAC_TRIGGER_NONE; // No trigger, free-running mode
sConfig.DAC_OutputBuffer = DAC_OUTPUTBUFFER_ENABLE;
if (HAL_DAC_ConfigChannel(&hdac, &sConfig, DAC_CHANNEL_1) != HAL_OK)
{
// Channel configuration Error
__BKPT();
}
// Enable DAC Channel and start the conversion
if (HAL_DAC_Start(&hdac, DAC_CHANNEL_1) != HAL_OK)
{
// Starting Error
__BKPT();
}
// Set DAC to some value, which won't be changed for this example
if (HAL_DAC_SetValue(&hdac, DAC_CHANNEL_1, DAC_ALIGN_12B_R, 3072) != HAL_OK)
{
// Setting DAC value Error
__BKPT();
}
}void Pulse_On() {
// Enable DAC
hdac.Instance->CR |= DAC_CR_EN1;
// Set GPIO to analog mode
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStruct = {0};
GPIO_InitStruct.Pin = GPIO_PIN_4;
GPIO_InitStruct.Mode = GPIO_MODE_ANALOG;
GPIO_InitStruct.Speed = GPIO_SPEED_FREQ_VERY_HIGH;
GPIO_InitStruct.Pull = GPIO_NOPULL;
HAL_GPIO_Init(GPIOA, &GPIO_InitStruct);
}
void Pulse_Off() {
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStruct = {0};
GPIO_InitStruct.Pin = GPIO_PIN_4;
GPIO_InitStruct.Mode = GPIO_MODE_OUTPUT_PP;
GPIO_InitStruct.Speed = GPIO_SPEED_FREQ_VERY_HIGH;
GPIO_InitStruct.Pull = GPIO_NOPULL;
HAL_GPIO_Init(GPIOA, &GPIO_InitStruct);
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOA, GPIO_PIN_4, GPIO_PIN_RESET);
// Clear EN1 bit of DAC_CR
hdac.Instance->CR &= ~DAC_CR_EN1;
}

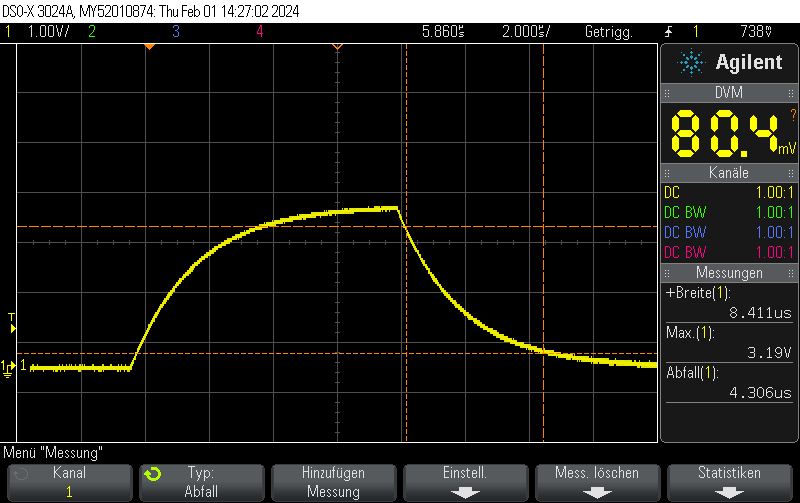
This oscilloscope trace was obtained by first setting the STM32H743ZI (Nucleo) DAC to 0x00, then setting it to maximum value (4096) without any intermediate steps.
The output buffer was enabled.
As can be seen on the trace, the rise/fall time is approximately 1us. No information about the clock speed etc is available for this example (Arduino on PlatformIO was used with standard settings). However, it does not appear that the rise/fall time is caused by the update rate. Setting the GPIO speed to maximum does not change the value.
This matches well with the datasheet-provided settling time of 1.7us(typ).
When disabling the output buffer, the result looks like this:
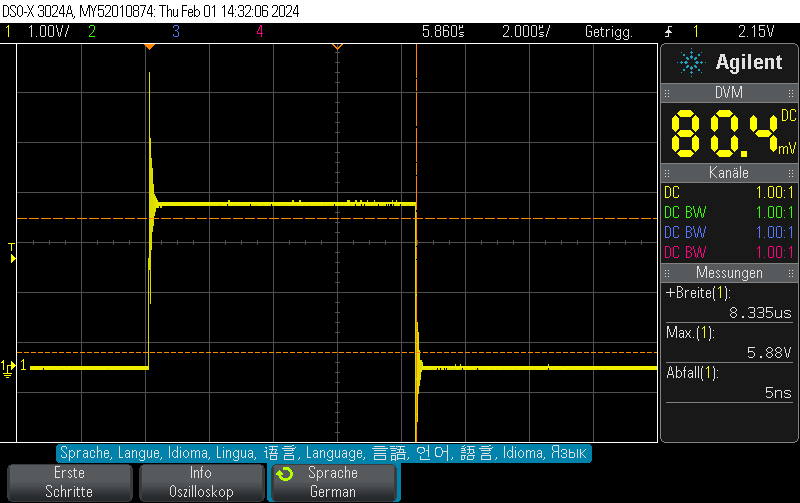
When, on the other hand, using the same pin as GPIO – using the exact same measurement setup (direct connection to BNC with 1M measurement impedance), the rise/fall time is almost zero.
// Function to initialize the DAC
void MX_DAC_Init(void)
{
DAC_ChannelConfTypeDef sConfig = {0};
// Initialize DAC
hdac.Instance = DAC1;
if (HAL_DAC_Init(&hdac) != HAL_OK)
{
// Initialization Error
__BKPT();
}
// Configure DAC channel
sConfig.DAC_Trigger = DAC_TRIGGER_NONE; // No trigger, free-running mode
sConfig.DAC_OutputBuffer = DAC_OUTPUTBUFFER_ENABLE;
if (HAL_DAC_ConfigChannel(&hdac, &sConfig, DAC_CHANNEL_1) != HAL_OK)
{
// Channel configuration Error
__BKPT();
}
// Enable DAC Channel and start the conversion
if (HAL_DAC_Start(&hdac, DAC_CHANNEL_1) != HAL_OK)
{
// Starting Error
__BKPT();
}
}The DAC value was set using
if (HAL_DAC_SetValue(&hdac, DAC_CHANNEL_1, DAC_ALIGN_12B_R, 4095) != HAL_OK) {
// Setting DAC value Error
__BKPT();
}
You can use How to print all preprocessor flags in PlatformIO to print preprocessor flags. You can find all ESP-IDF related flags using
cat .pio/build/esp32dev/src/main.o | grep IDF
which is – with an empty main.c file just
#define IDF_VER "5.1.2"
Note that IDF_VER is also defined for Arduino since it is used internally by Arduino.
So you can use the following check which distinguistes between Arduino & ESP-iDF
#if !defined(ARDUINO) && defined(IDF_VER) // ESP-IDF code goes here #else // Non-ESP-IDF code goes here #else
You can use How to print all preprocessor flags in PlatformIO to print preprocessor flags. Note that these include the flags #defined in #includes such as Arduino.h. You can remove everything from main.cpp, however, so only the flags defined by the build environment are visible.
The Arduino-related flags are
#define ARDUINO_VARIANT "esp32" #define ARDUINO_ARCH_ESP32 1 #define ARDUINO_PARTITION_default 1 #define ARDUINO 10812 #define ARDUINO_ESP32_DEV 1 #define ARDUINO_BOARD "Espressif ESP32 Dev Module"
So if you want a platform-independent check for Arduino, use
#ifdef ARDUINO // Arduino code goes here #else // Non-Arduino code goes here #else
This example configures ADC1 to read a 16 bit analog value of PA7 using a polled loop. The serial output is available on the STLink header.
#include <Arduino.h>
#include <stm32h7xx_hal.h>
ADC_HandleTypeDef hadc1;
static void MX_GPIO_Init(void)
{
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStruct = {0};
// Enable the GPIOA clock
__HAL_RCC_GPIOA_CLK_ENABLE();
/**ADC1 GPIO Configuration
PA7 ------> ADC1_IN7
*/
GPIO_InitStruct.Pin = GPIO_PIN_7;
GPIO_InitStruct.Mode = GPIO_MODE_ANALOG;
GPIO_InitStruct.Pull = GPIO_NOPULL;
HAL_GPIO_Init(GPIOA, &GPIO_InitStruct);
}
static void MX_ADC1_Init(void)
{
ADC_ChannelConfTypeDef sConfig = {0};
hadc1.Instance = ADC1;
hadc1.Init.ClockPrescaler = ADC_CLOCK_SYNC_PCLK_DIV4;
hadc1.Init.Resolution = ADC_RESOLUTION_16B;
hadc1.Init.ScanConvMode = ADC_SCAN_DISABLE;
hadc1.Init.EOCSelection = ADC_EOC_SINGLE_CONV;
hadc1.Init.LowPowerAutoWait = DISABLE;
hadc1.Init.ContinuousConvMode = DISABLE;
hadc1.Init.NbrOfConversion = 1;
hadc1.Init.DiscontinuousConvMode = DISABLE;
hadc1.Init.ExternalTrigConv = ADC_SOFTWARE_START;
hadc1.Init.ExternalTrigConvEdge = ADC_EXTERNALTRIGCONVEDGE_NONE;
//hadc1.Init.DMAContinuousRequests = DISABLE;
hadc1.Init.Overrun = ADC_OVR_DATA_OVERWRITTEN;
hadc1.Init.OversamplingMode = DISABLE;
if (HAL_ADC_Init(&hadc1) != HAL_OK)
{
// Initialization Error
}
sConfig.Channel = ADC_CHANNEL_7;
sConfig.Rank = ADC_REGULAR_RANK_1;
sConfig.SamplingTime = ADC_SAMPLETIME_2CYCLES_5;
sConfig.SingleDiff = ADC_SINGLE_ENDED;
sConfig.OffsetNumber = ADC_OFFSET_NONE;
sConfig.Offset = 0;
if (HAL_ADC_ConfigChannel(&hadc1, &sConfig) != HAL_OK)
{
// Channel Configuration Error
}
}
void setup() {
HAL_Init();
SystemClock_Config();
MX_GPIO_Init();
MX_ADC1_Init();
Serial.begin(115200);
}
void loop() {
HAL_ADC_Start(&hadc1); // Start ADC conversion
HAL_ADC_PollForConversion(&hadc1, HAL_MAX_DELAY); // Wait for conversion to complete
uint32_t adcValue = HAL_ADC_GetValue(&hadc1); // Read the ADC converted value
Serial.printf("ADC value: %04X\n", adcValue);
}[env:nucleo_h743zi] platform = ststm32 board = nucleo_h743zi framework = arduino monitor_speed = 115200
Example output (unconnected):
ADC value: 04B6 ADC value: 049C ADC value: 04AC ADC value: 04AE ADC value: 0497 ADC value: 04AF ADC value: 04A7 ADC value: 04C6 ADC value: 0491 ADC value: 04A1 ADC value: 04AF ADC value: 0493 ADC value: 0497 ADC value: 04AF ADC value: 04A3 ADC value: 047D ADC value: 04C1 ADC value: 04B1 ADC value: 04AF ADC value: 0498 ADC value: 04A1 ADC value: 04C3 ADC value: 04AE ADC value: 04AC ADC value: 0489 ADC value: 0491 ADC value: 0491 ADC value: 047E ADC value: 04B8 ADC value: 0494 ADC value: 04A5 ADC value: 0491 ADC value: 0494 ADC value: 048A ADC value: 0499 ADC value: 0494 ADC value: 049E
While building a software project using cmake, you see error messages like
CMake Error at /usr/share/cmake-3.25/Modules/FindPackageHandleStandardArgs.cmake:230 (message): Could NOT find HarfBuzz (missing: HarfBuzz_INCLUDE_DIR HarfBuzz_LIBRARY _HarfBuzz_REQUIRED_LIBS_FOUND) Call Stack (most recent call first): /usr/share/cmake-3.25/Modules/FindPackageHandleStandardArgs.cmake:600 (_FPHSA_FAILURE_MESSAGE) cmake/FindHarfBuzz.cmake:153 (find_package_handle_standard_args) CMakeLists.txt:801 (find_package)
Install libharfbuzz-dev
sudo apt -y install libharfbuzz-dev
While building a software project using cmake, you see error messages like
CMake Error at /usr/share/cmake-3.25/Modules/FindPackageHandleStandardArgs.cmake:230 (message): Could NOT find GLM (missing: GLM_INCLUDE_DIR GLM_VERSION) (Required is at least version "0.9.8") Call Stack (most recent call first): /usr/share/cmake-3.25/Modules/FindPackageHandleStandardArgs.cmake:600 (_FPHSA_FAILURE_MESSAGE) cmake/FindGLM.cmake:54 (FIND_PACKAGE_HANDLE_STANDARD_ARGS) CMakeLists.txt:751 (find_package)
Install libglm-dev
sudo apt -y install libglm-dev