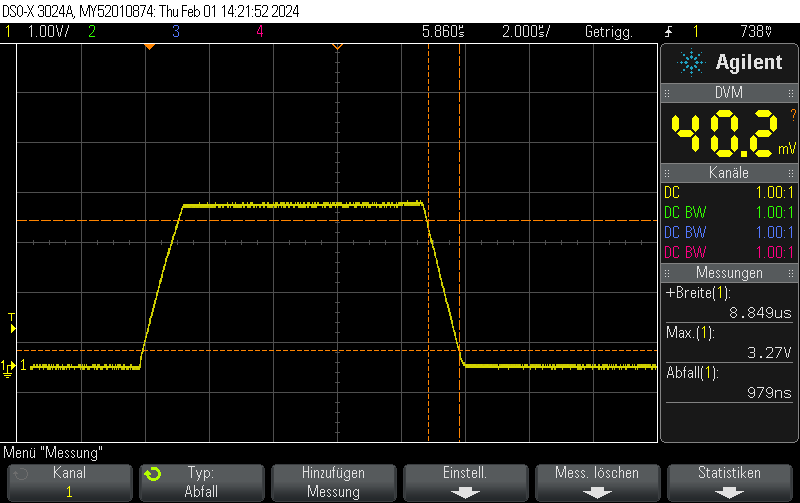
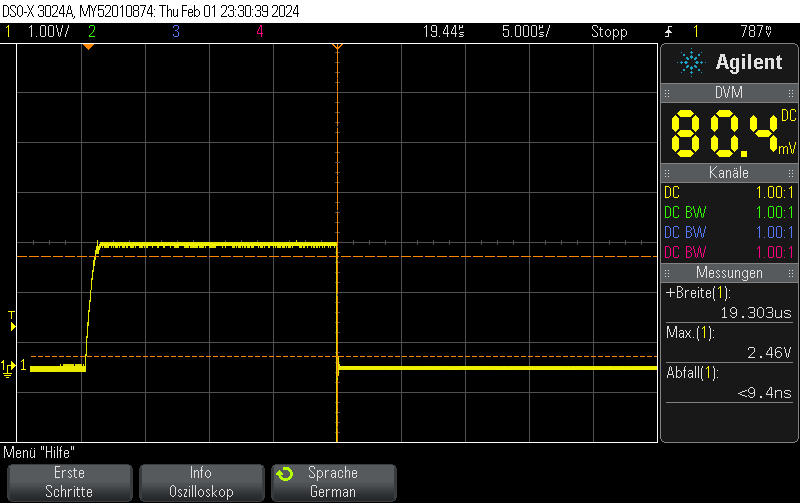
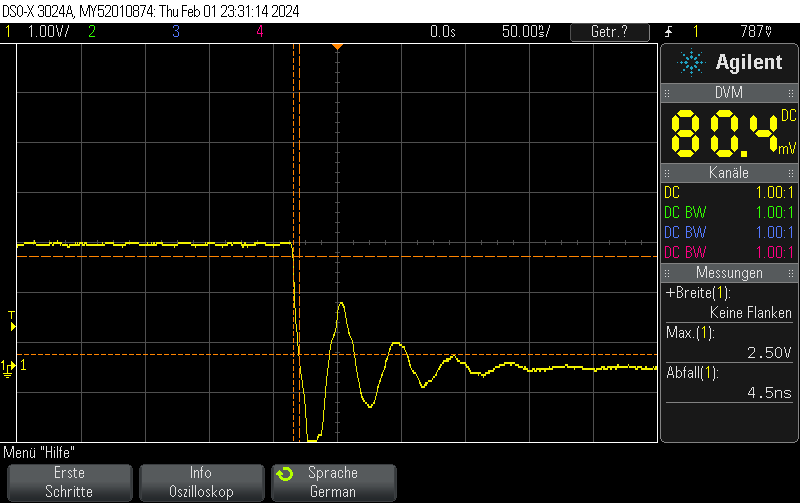
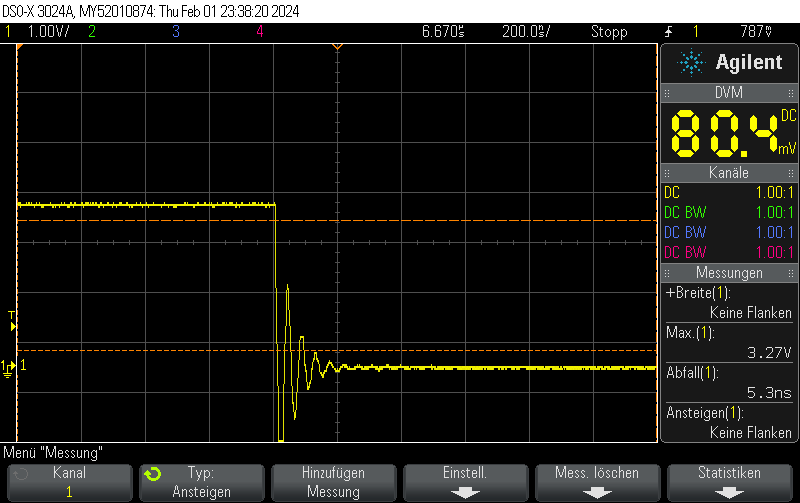
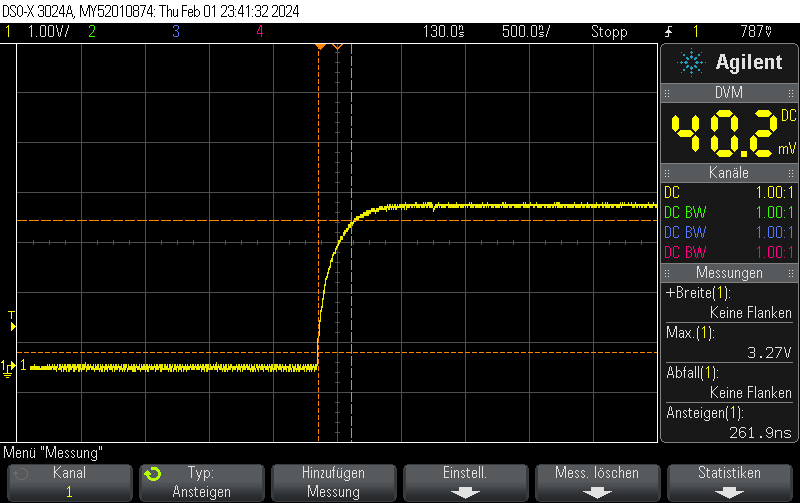
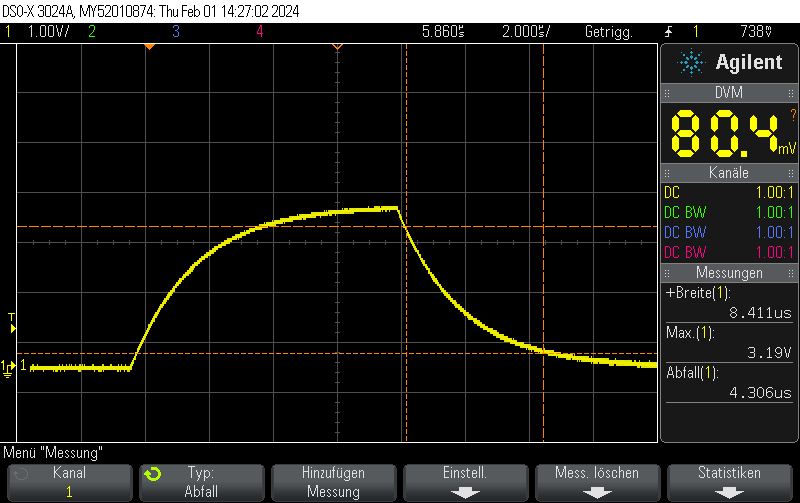
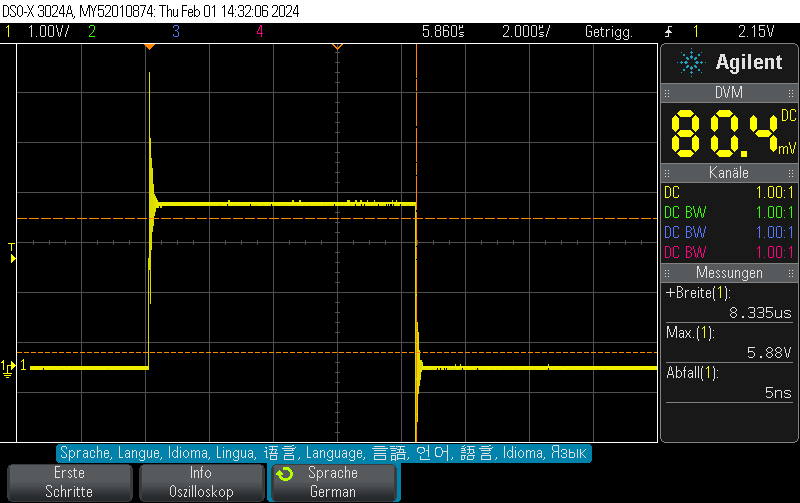
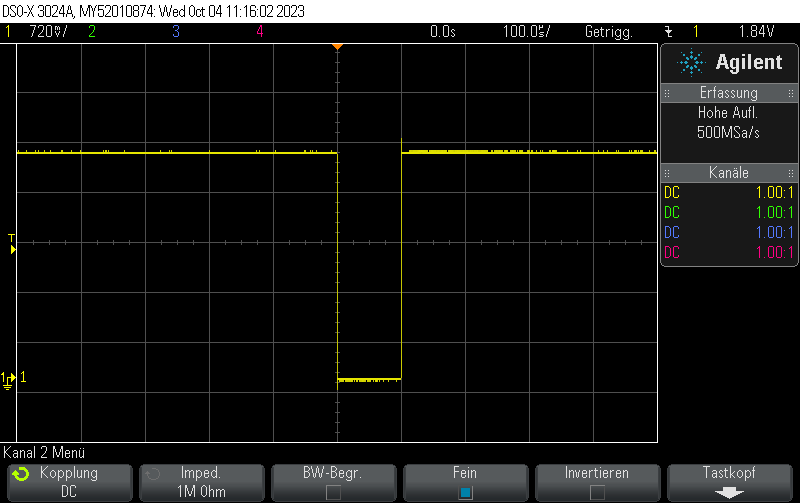
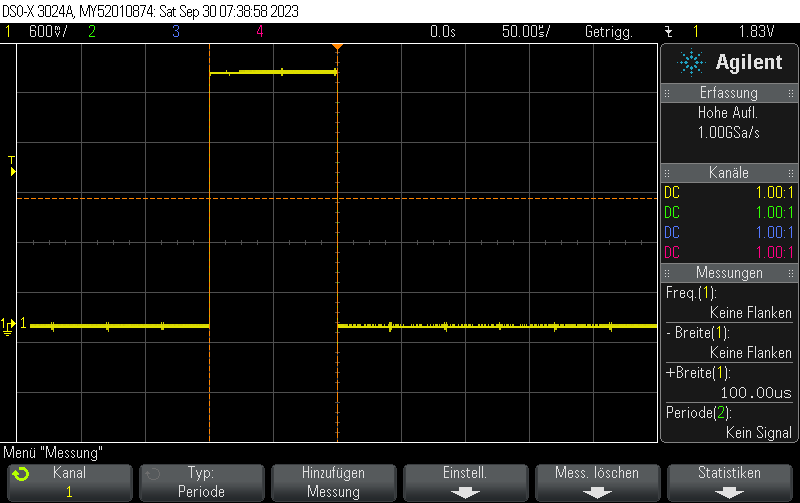
This pulse generator firmware uses methods discussed e.g. in Short pulse generation with Arduino Uno Part 4: NOP for loops to generate both dynamic (for loops of NOP instructions) and static (template-based automatically unrolled) in a combined manner so you can select more or less any pulse width using a high resolution.
It doesn’t work 100% since there are still some pulse width jumps. However, it is still useful for many microsecond 5V pulse generation applications and might also be a useful technology demonstrator for hybrid static/dynamic pulsers using optimized integer template loop unrolling approaches.
In order to control the pulse width, open a serial interface and type + to increase the pulse width or - to decrease the pulse width.
This might work on Arduino Unos as well but my Uno had a broken serial interface chip so I used a ATMega2560 board.
// License: CC0 1.0 Universal
// By Uli Köhler (techoverflow.net)
#include <Arduino.h>
#include <avr/io.h>
#include <ArduinoJson.h>
#define PORT13 PORTB
#define PIN13 7
#define PIN13_MASK (1 << PIN13)
#define PORT11 PORTB
#define PIN11 5
#define PIN11_MASK (1 << PIN11)
int pulseLength = 1;
using PulseFunc = void (*)(int);
// Function pointer to void(int)
PulseFunc pulser = nullptr;
int pulserParam = 0; // Pre-computed parameter for the pulser function
void DoNothingPulser(int _) {
}
/**
* Pulse the output pin, for very short pulses.
* Will ONLY perform static (optimized) NOPs.
* Will NOT perform dynamic (slower) NOP cycles
*
* Hence, this function does not have any overhead from for loops.
*/
template<int nNOPs>
void PulseStatic(int _) {
cli();
PORT11 |= PIN11_MASK;
// Static for loop (optimized out - template-driven)
// Force unrolling of the loop
// NOTE: Compiler will only unroll for n < 8
for (int i = 0; i < min(nNOPs, 6); i++) {
_NOP();
}
if(nNOPs > 6) {
for (int i = 0; i < nNOPs - 6; i++) {
_NOP();
}
}
PORT11 &= ~PIN11_MASK;
sei();
}
/**
* Pulse the output pin, for very short pulses.
* Will perform static (optimized) NOPs and
* also dynamic (slower) NOP cycles
*/
template<int nNOPs>
void PulseDynamic(int dynamicNOPs) {
cli();
PORT11 |= PIN11_MASK;
// Dynamic for loop (NOT optimized out - template-driven)
for (int i = 0; i < dynamicNOPs; i++)
{
_NOP();
}
// Static for loop (optimized out - template-driven)
// Force unrolling of the loop
// NOTE: Compiler will only unroll for n < 8
for (int i = 0; i < min(nNOPs, 6); i++) {
_NOP();
}
if(nNOPs > 6) {
for (int i = 0; i < nNOPs - 6; i++) {
_NOP();
}
}
PORT11 &= ~PIN11_MASK;
sei();
}
PulseFunc staticPulsers[] = {
DoNothingPulser,
&PulseStatic<0>, // 0 NOPs
&PulseStatic<1>, // 1 NOPs ...
&PulseStatic<2>,
&PulseStatic<3>,
&PulseStatic<4>,
&PulseStatic<5>,
&PulseStatic<6>,
&PulseStatic<7>,
&PulseStatic<8>,
&PulseStatic<9>,
&PulseStatic<10>,
&PulseStatic<11>
};
PulseFunc dynamicPulsers[] = {
&PulseDynamic<0>,
&PulseDynamic<1>,
&PulseDynamic<2>,
&PulseDynamic<3>,
&PulseDynamic<4>,
&PulseDynamic<5>,
&PulseDynamic<6>,
&PulseDynamic<7>,
&PulseDynamic<8>,
&PulseDynamic<9>,
&PulseDynamic<10>,
&PulseDynamic<11>
};
constexpr int A = 7;
constexpr int B = 6;
void ReconfigurePulse() {
// Very short pulses are performed using only static
if(pulseLength < A) {
pulser = staticPulsers[pulseLength];
} else {
pulser = dynamicPulsers[(pulseLength - A) % B];
pulserParam = (pulseLength - A) / B;
}
}
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.setTimeout(25);
ReconfigurePulse(); // with default pulseLength
pinMode(11, OUTPUT);
pinMode(LED_BUILTIN, OUTPUT);
}
void loop()
{
pulser(pulserParam);
Serial.println(pulseLength);
//ProcessSerialInput();
// Wait until 50ms has passed since start
while(Serial.available() > 0) {
int c = Serial.read();
if(c == '+') {
pulseLength++;
ReconfigurePulse();
} else if(c == '-') {
pulseLength--;
if(pulseLength < 0) {pulseLength = 0;}
ReconfigurePulse();
}
}
delay(50);
}