You can download a ISO containing Windows KVM guest drivers on the fedora repository.
Virtualization
XenOrchestra default username/password credentials
The default username/password for XenOrchestra are:
- Username:
[email protected] - Password:
admin
How to install VirtualBox extension pack (.vbox-extpack) on the command line (headless)
Use the following command to install a VirtualBox extension pack on a server or other headless machine:
sudo vboxmanage extpack install [filename]
for example
sudo vboxmanage extpack install Oracle_VM_VirtualBox_Extension_Pack-7.0.8.vbox-extpack
How to set screen size for UEFI VMs on XCP-NG
The following sequence allows you to enter the UEFI setup and set the screen size. It does not work for VMs running BIOS!
- Open the VM’s console
- Start the VM
- Immediately start pressing
F2repeatedly until you see the UEFI setup screen: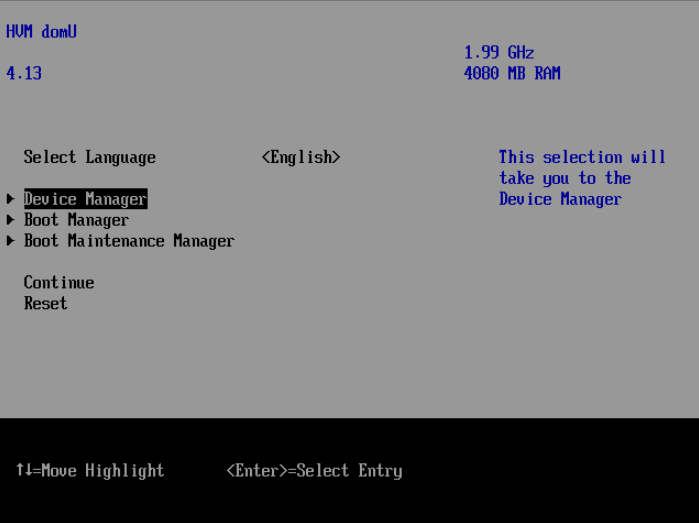
- Enter the
Device Manager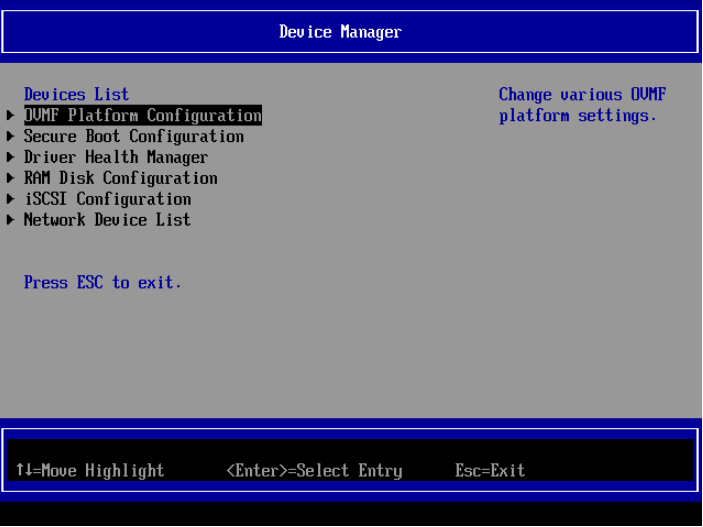
- Enter
OVMF Platform Configurationand select the screen resolution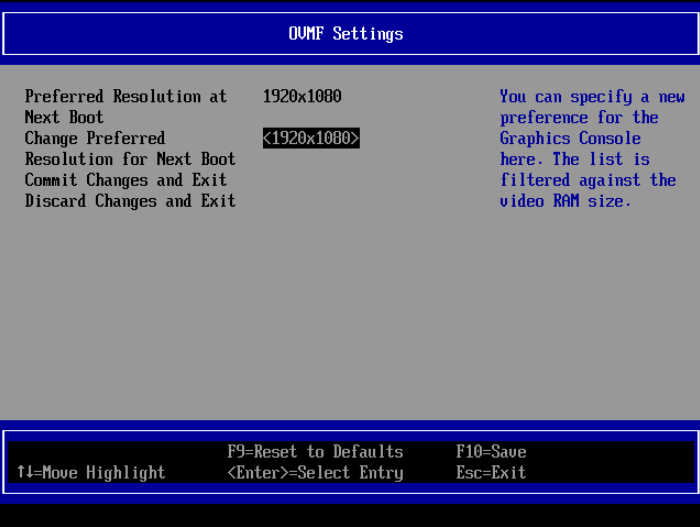
- Exit by pressing
ESCand selectYto save the changes. Continue pressingESCuntil you are at the start screen.
- Now select
Resetand wait for the OS to boot. You need to selectResetbecause the change will only be effective after the next complete reboot.
How to disable XCP-NG Windows Update PCIe device on the command line
This post shows you how to disable the XCP-NG windows update device on the command line. This prevents automatic installation of the Citrix drivers, enabling manual install of a custom version.
Note that you can easily disable the Windows update PCIe device in XenOrchestra using a single click, but not in XCP-NG center!
Prerequisite: Shut down the VM in question – usually you need to disable the device before installing Windows!
First, get the UUID of the VM usinjg
xe vm-list
which will output, for each virtual machine, something like:
uuid ( RO) : 98002b8d-070f-9638-071c-be7e6c82f6a3
name-label ( RW): CoreOS
power-state ( RO): runningFrom that, copy the UUID such as 98002b8d-070f-9638-071c-be7e6c82f6a3.
Now run:
xe vm-param-set uuid=YOURUUID has-vendor-device=false
for example,
xe vm-param-set uuid=98002b8d-070f-9638-071c-be7e6c82f6a3 has-vendor-device=false
Now you can startup your VM with the driver installation PCIe device being disabled.
XenOrchestra docker-compose setup with Traefik labels
Based on Simple XenOrchestra setup using docker-compose, this extension of our config from that post features Traefik container labels. For the Traefik configuration, see for example our previous post Simple Traefik docker-compose setup with Lets Encrypt Cloudflare DNS-01 & TLS-ALPN-01 & HTTP-01 challenges
This setup uses a Wildcard certificate but you can also use a non-wildcard cert (e.g. if you don’t have access to the DNS for the DNS01 challenge) by just deleting both traefik.http.routers.xenorchestra.tls.domains... lines and selecting a suitable resolver.
version: '3'
services:
xen-orchestra:
restart: unless-stopped
image: ronivay/xen-orchestra:latest
container_name: xen-orchestra
network_mode: host
stop_grace_period: 1m
environment:
- HTTP_PORT=1780
cap_add:
- SYS_ADMIN
security_opt:
- apparmor:unconfined
volumes:
- ./xo-data:/var/lib/xo-server
- ./redis-data:/var/lib/redis
labels:
- "traefik.enable=true"
- "traefik.http.routers.xenorchestra.rule=Host(`xenorchestra.mydomain.com`)"
- "traefik.http.routers.xenorchestra.entrypoints=websecure"
- "traefik.http.routers.xenorchestra.tls.certresolver=cloudflare"
- "traefik.http.routers.xenorchestra.tls.domains[0].main=mydomain.com"
- "traefik.http.routers.xenorchestra.tls.domains[0].sans=*.mydomain.com"
- "traefik.http.services.xenorchestra.loadbalancer.server.port=1780"
You can now login with the default credentials: [email protected] and password admin
How to install tailscale on XCP-NG host
By installing tailscale on XCP-NG hosts, you can provide easier access to your virtualization host using VPN.
Run the following commands via SSH as root on the XCP-NG host:
sudo yum-config-manager --add-repo https://pkgs.tailscale.com/stable/centos/7/tailscale.repo sudo yum -y install tailscale
and enable & start the tailscale daemon tailscaled:
systemctl enable --now tailscaled
How to install Xen guest utilities on Ubuntu
On Ubuntu 22.04, this package is not available any more and the best way to install it that is known to me at the moment is to use the guest tools ISO.
Install the package using
sudo apt -y install xe-guest-utilities
Now reboot, which will automatically start the management agent service:
sudo reboot
Simple XenOrchestra setup using docker-compose
Also see this variant with Traefik reverse proxy config: XenOrchestra docker-compose setup with Traefik labels
Create a directory such as /opt/xenorchestra and create docker-compose.yml:
version: '3'
services:
xen-orchestra:
restart: unless-stopped
image: ronivay/xen-orchestra:latest
container_name: xen-orchestra
network_mode: host
stop_grace_period: 1m
environment:
- HTTP_PORT=1780
cap_add:
- SYS_ADMIN
security_opt:
- apparmor:unconfined
volumes:
- ./xo-data:/var/lib/xo-server
- ./redis-data:/var/lib/redisYou can choose any HTTP port you want using HTTP_PORT=1780. In this case, we opted for using network_mode: host to bypass the docker networking, since XenOrchestra seems to work better with full network access instead of the container having an own IP.
Now you can use our script from Create a systemd service for your docker-compose project in 10 seconds to automatically start XenOrchestra on boot (and start it immediately):
curl -fsSL https://techoverflow.net/scripts/create-docker-compose-service.sh | sudo bash /dev/stdin
Now access https://<IP of controller>:1780 (or your custom HTTP port) to get started with the XO setup.
How to find XCP-NG host-uuid
For many xe commands on XCP-NG you have to use a host-uuid=... parameter.
In order to find out your Host UUID, use
xe host-list
Example:
[03:19 virt01-xcpng ~]# xe host-list
uuid ( RO) : 71739b18-2999-4794-a024-87d5d26215d1
name-label ( RW): virt01-xcpng
name-description ( RW): Default installIn this example, the Host UUID of the only host is 71739b18-2999-4794-a024-87d5d26215d1.
How to install xenutils on Linux (XCP-NG)
Using CoreOS? See this post instead!
First, insert the guest-tools.iso supplied with XCP-NG into the DVD drive of the virtual machine.
Then run these commands. Note that this will reboot the machine after it finished
sudo mount -o ro /dev/sr0 /mnt/ cd /mnt/Linux sudo ./install.sh -n sudo reboot
After the VM reboots, XCP-NG should detect the management agent.
Please eject the guest tools medium from the machine after the reboot! Sometimes unneccessarily mounted media cause issues.
Fedora CoreOS minimal ignition config for XCP-NG
This is the Ignition config that I use to bring up my Fedora CoreOS instance on a VM on my XCP-NG server:
{
"ignition": {
"version": "3.2.0"
},
"passwd": {
"users": [
{
"groups": [
"sudo",
"docker"
],
"name": "uli",
"sshAuthorizedKeys": [
"ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAAAgQDpvDSxIwnyMCFtIPRQmPUV6hh9lBJUR0Yo7ki+0Vxs+kcCHGjtcgDzcaHginj1zvy7nGwmcuGi5w83eKoANjK5CzpFT4vJeiXqtGllh0w+B5s6tbSsD0Wv3SC9Xc4NihjVjLU5gEyYmfs/sTpiow225Al9UVYeg1SzFr1I3oSSuw== sample@host"
]
}
]
},
"storage": {
"files": [
{
"path": "/etc/hostname",
"contents": {
"source": "data:,coreos-test%0A"
},
"mode": 420
},
{
"path": "/etc/profile.d/systemd-pager.sh",
"contents": {
"source": "data:,%23%20Tell%20systemd%20to%20not%20use%20a%20pager%20when%20printing%20information%0Aexport%20SYSTEMD_PAGER%3Dcat%0A"
},
"mode": 420
},
{
"path": "/etc/sysctl.d/20-silence-audit.conf",
"contents": {
"source": "data:,%23%20Raise%20console%20message%20logging%20level%20from%20DEBUG%20(7)%20to%20WARNING%20(4)%0A%23%20to%20hide%20audit%20messages%20from%20the%20interactive%20console%0Akernel.printk%3D4"
},
"mode": 420
}
]
},
"systemd": {
"units": [
{
"enabled": true,
"name": "docker.service"
},
{
"enabled": true,
"name": "containerd.service"
},
{
"dropins": [
{
"contents": "[Service]\n# Override Execstart in main unit\nExecStart=\n# Add new Execstart with `-` prefix to ignore failure\nExecStart=-/usr/sbin/agetty --autologin core --noclear %I $TERM\nTTYVTDisallocate=no\n",
"name": "autologin-core.conf"
}
],
"name": "[email protected]"
}
]
}
}
Which is build from this YAML:
variant: fcos
version: 1.2.0
passwd:
users:
- name: uli
groups:
- "sudo"
- "docker"
ssh_authorized_keys:
- "ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAAAgQDpvDSxIwnyMCFtIPRQmPUV6hh9lBJUR0Yo7ki+0Vxs+kcCHGjtcgDzcaHginj1zvy7nGwmcuGi5w83eKoANjK5CzpFT4vJeiXqtGllh0w+B5s6tbSsD0Wv3SC9Xc4NihjVjLU5gEyYmfs/sTpiow225Al9UVYeg1SzFr1I3oSSuw== sample@computer"
systemd:
units:
- name: docker.service
enabled: true
- name: containerd.service
enabled: true
- name: [email protected]
dropins:
- name: autologin-core.conf
contents: |
[Service]
# Override Execstart in main unit
ExecStart=
# Add new Execstart with `-` prefix to ignore failure
ExecStart=-/usr/sbin/agetty --autologin core --noclear %I $TERM
TTYVTDisallocate=no
storage:
files:
- path: /etc/hostname
mode: 0644
contents:
inline: |
coreos-test
- path: /etc/profile.d/systemd-pager.sh
mode: 0644
contents:
inline: |
# Tell systemd to not use a pager when printing information
export SYSTEMD_PAGER=cat
- path: /etc/sysctl.d/20-silence-audit.conf
mode: 0644
contents:
inline: |
# Raise console message logging level from DEBUG (7) to WARNING (4)
# to hide audit messages from the interactive console
kernel.printk=4using
fcct --pretty --strict ignition.yml --output ignition.ign
or TechOverflow’s online transpiler tool.
Install using:
sudo coreos-installer install /dev/xvda --copy-network --ignition-url https://mydomain.com/ignition.ign
Features:
- DHCP on all network interfaces
- TTY on the screen
- No password – remember to replace the SSH key by your key!
How to install XCP-NG xe-guest-utilities on Fedore CoreOS using guest-tools.iso
Important note: While installing the Xen utilities using the CD ISO still works, it is outdated and you should prefer installing it using the rpm package. See our post Fedora CoreOS: How to install Xen/XCP-NG guest utilities using rpm-ostree
First, insert the guest-tools.iso supplied with XCP-NG into the DVD drive of the virtual machine.
Then run this sequence of commands to install. Note that this will reboot the CoreOS instance!
curl -fsSL https://techoverflow.net/scripts/install-xenutils-coreos.sh | sudo bash /dev/stdin
This will run the following script:
sudo mount -o ro /dev/sr0 /mnt sudo rpm-ostree install /mnt/Linux/*.x86_64.rpm sudo cp -f /mnt/Linux/xen-vcpu-hotplug.rules /etc/udev/rules.d/ sudo cp -f /mnt/Linux/xe-linux-distribution.service /etc/systemd/system/ sudo sed 's/share\/oem\/xs/sbin/g' -i /etc/systemd/system/xe-linux-distribution.service sudo systemctl daemon-reload sudo systemctl enable /etc/systemd/system/xe-linux-distribution.service sudo umount /mnt sudo systemctl reboot
After rebooting the VM, XCP-NG should detect the management agent.
Based on work by steniofilho on the Fedora Forum.
Please eject the guest tools medium from the machine after the reboot! Sometimes unneccessarily mounted media cause issues.
How to list VMs in XCP-NG on the command line
In order to list VMs on the command line, login to XCP-NG using SSH and run this command:
xe vm-list
Example output:
[16:51 virt01-xcpng ~]# xe vm-list
uuid ( RO) : 56dc99f2-c617-f7a9-5712-a4c9df54229a
name-label ( RW): VM 1
power-state ( RO): running
uuid ( RO) : 268d56ab-9672-0f45-69ae-efbc88380b21
name-label ( RW): VM2
power-state ( RO): running
uuid ( RO) : 9b1a771f-fb84-8108-8e01-6dac0f957b19
name-label ( RW): My VM 3
power-state ( RO): running
How to fix XCP-NG XENAPI_MISSING_PLUGIN(xscontainer) or Error on getting the default coreOS cloud template
Problem:
When creating a CoreOS container on your XCP-NG host, XCP-NG center or XenOrchestra tells you
Cloud config: Error on getting the default coreOS cloud template
with the error message
XENAPI_MISSING_PLUGIN(xscontainer) This is a XenServer/XCP-ng error
Solution:
Log into the host’s console as root using SSH or the console in XCP-NG center or XenOrchestra and run
yum install xscontainer
After that, reload the page (F5) you use to create your container. No host restart is required.
Note that if you have multiple hosts, you need to yum install xscontainer for each host individually.
How to download a file or directory from a LXC container
To download files, use
lxc file pull <container name>/<path>/<filename> <target directory>
To download directories, use
lxc file pull --recursive <container name>/<path>/<filename> <target directory>
Examples:
Download /root/myfile.txt from mycontainer to the current directory (.):
lxc file pull mycontainer/root/myfile.txt .
Download /root/mydirectory from mycontainer to the current directory (.):
lxc file pull -r mycontainer/root/mydirectory .
Launching Debian containers using LXC on Ubuntu
Problem:
You know you can launch an Ubuntu LXC container using
lxc launch ubuntu:18.04 myvm
Now you want to launch a Debian VM using
lxc launch debian:jessie myvm
but you only get this error message:
Error: The remote "debian" doesn't exist
Solution:
The debian images are (by default) available from the images remote, not the debian remote, so you need to use this:
lxc launch images:debian/jessie myvm
How to fix lxd ‘Failed container creation: No storage pool found. Please create a new storage pool.’
Problem:
You want to launch some lxd container using lxc launch […] but instead you get the following error message:
Failed container creation: No storage pool found. Please create a new storage pool.
Solution:
You need to initialize lxd before using it:
lxd init
When it asks you about the backend
Name of the storage backend to use (btrfs, dir, lvm) [default=btrfs]:
choosing the default option (btrfs) means that you’ll have to use a dedicated block device (or a dedicated preallocated file image) for storage. While this is more efficient if you run many containers at a time, I recommend to choose the dir backend for the default storage pool, because that option will be easiest to configure and will not occupy as much space on your hard drive.
See Storage management in lxd for more more details, including different options for storage pools in case you need a more advanced setup.